Editorial
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious disease
caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). It was
first identified in December 2019 in Wuhan, China, and has since spread
globally, resulting in an ongoing pandemic [1–2].
As of May 12, 2020, more than 4.23 million cases have been reported across 187
countries and territories, resulting in more than 289,000 deaths. More than
1.48 million people have recovered [3].
Alkaline foods: All
foods can be divided into acidic, neutral, or alkaline. A food’s pH isn’t
measured by its physical properties, but by the residue (final products) that’s
left in the body once the food has been metabolized.
For example, we would intuitively
consider lemon acidic because it has a sour taste and the ability to erode our
tooth enamel. However, once it has been metabolized by the body, lemon leaves
the blood alkaline. This explains why a seemingly acidic food can “turn”
alkaline in the body.
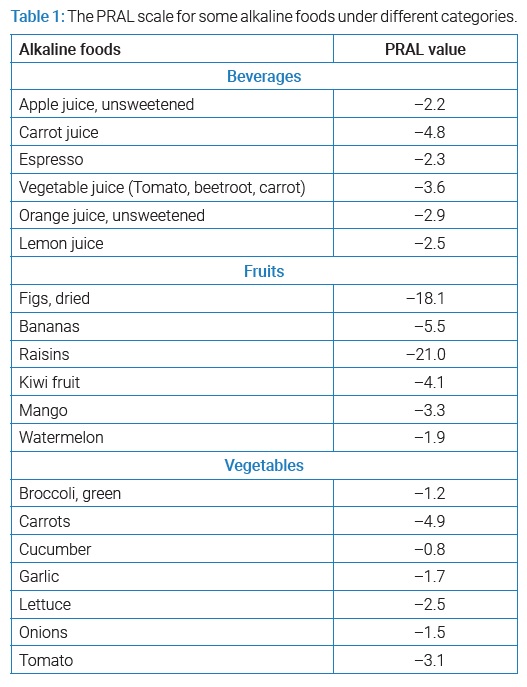
To determine whether a food is
alkalizing or acidic to the body, each food is measured on a PRAL scale,
“Potential Renal Acid Load,” as shown in (Table 1).
Usually, alkaline foods list was divided into three sections. a) Strong
alkaline foods; b) Medium alkaline foods; and c) Poor alkaline foods.
The relation between the alkaline foods, immunity and Covid-19
virus.
The British Dietetic Association
(BDA) has stated no specific food or supplements can prevent a person from
catching COVID-19. Alongside WHO advice, the BDA encourages people to consume a
healthy, balanced diet to support the immune system.
Healthy and varied alkaline foods as
mentioned in (Table 1) containing the five
main groups can help provide most people with the nutrients they need. Most of
the nutrients we already get from our regular diet (including copper, folate,
iron, zinc, selenium, and vitamins A, B6, B12, C, and D) are all involved in
maintaining healthy immune function. Moreover, we also advise adults (living in
quarantine) to take a daily supplement of 10 μg of vitamin D and eat vitamin D
rich foods, like oily fish, egg yolks, and fortified breakfast cereals to
ensure adequate vitamin D levels. This is because of the effect of vitamin D on
the immune system and its ability to prevention COVID-19 infection.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Informed consent was obtained for this publication.
Keywords
Alkaline
foods; Coronavirus; Immunity
Cite this article
Shalaby
EA, Shalaby HE. The alkaline foods and its relation with immunity and COVID-19
virus during quarantine time. Clin Oncol J. 2021;2(2);1−2.
Copyright
©
2021 Emad A. Shalaby. This is an open access article distributed under the
terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC
BY-4.0).

